Note: This article’s statistics come from third-party sources and do not represent the opinions of this website.
Milk is a high commodity around the world, and of course, milk comes from cows. Have you ever stopped to wonder just how many dairy cows there are in the United States? Better yet, in the world?
Cows are an important food source for humans. There are about 270 million dairy cows globally and concerns are never-ending on how they are treated. The number of licensed dairy farms is declining in the U.S.; however, milk production is increasing. It doesn’t make sense, does it? The demand for increased milk production causes more stress on cows, leading to medical conditions, such as lameness and mastitis.
In this article, we’ll look at the statistics of the dairy cow and shed some light on these statistics, and some of them may surprise you.
The 14 Dairy Cow Statistics
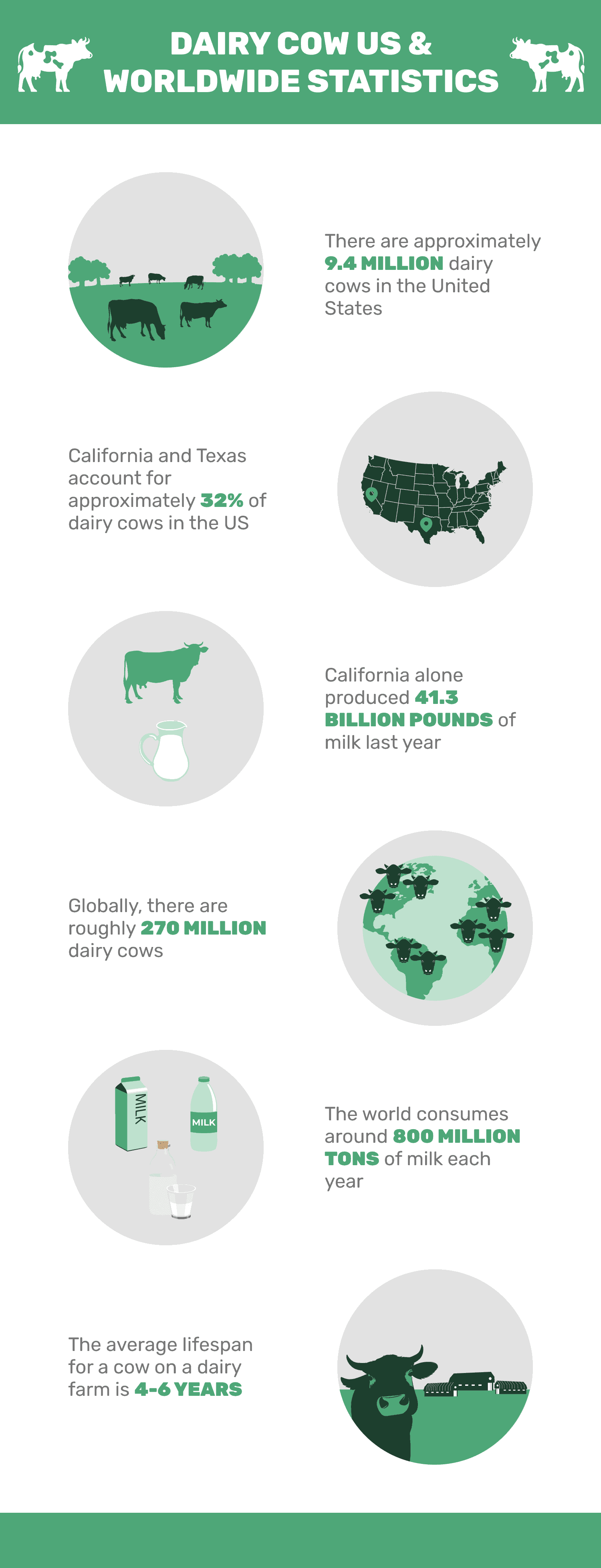
- There are roughly 270 million dairy cows globally.
- There are approximately 9.4 million dairy cows in the United States.
- California produced 41.3 billion pounds of milk in 2021.
- California and Texas account for approximately 32% of dairy cows in the United States.
- The western and northern parts of the U.S. account for 50% of the U.S. milk supply.
- Since 2003, the U.S. has lost more than 50% of licensed dairy farms.
- In 2020, the U.S. dairy industry was worth 40.5 billion.
- The world consumes 800 million tons of milk each year
- Over the last decade, the mortality rate of dairy herds ranged from 2% to 15% across the United States.
- The average natural lifespan of a cow is 15 to 20 years.
- The average lifespan for a cow on a dairy farm is 4 to 6 years.
- Dairy cow slaughters accounted for 9.5% of federally inspected slaughters in 2020.
- The number of cubicles should exceed the number of cows in housing areas by 5%.
- Lameness on U.S. dairy farm cattle ranges from 13% to 55%.

Cow Populations in the U.S. and the World
1. There are roughly 270 million dairy cows globally.
(World Wildlife Fund)
Milk production is a global industry and in high demand. Milk production is a high commodity due to population growth, the westernization of diets in China and India, and rising incomes.

2. There are approximately 9.4 million dairy cows in the United States.
(United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)
The United States is filled with farmland, and if you think about it, you’ll find cows grazing just about anywhere you go. Cows serve an important purpose; they’re not used just for dairy but for beef production, as well. In the first part of 2021, the number of cows increased by 144,000.
3. California produced 41.3 billion pounds of milk in 2021.
(Beef2Live)
When you think of California, cows probably do not come to mind, but the Golden State had 1,725,000 dairy cows as of 2020 and has the most dairy cows in the U.S. Spanish Missionaries brought them to the state in the 1700s, and cows have been producing milk there since.
4. California and Texas account for approximately 32% of dairy cows in the United States.
(Comptroller.Texas.Gov)
Texas currently ranks fifth in the United States for dairy cows. However, even though Texas has recently seen a decrease in dairy farms, the 351 dairy farms have produced 14.8 billion pounds of milk in 2020 alone.

Global Milk Production
5. The western and northern parts of the U.S. account for 50% of the U.S. milk supply.
(USDA)
In 2020, the most milk-producing states in the top five were: California, Wisconsin, Idaho, New York, and Texas. These states account for over 50% of the United States milk supply.
6. Since 2003, the U.S. has lost more than 50% of licensed dairy farms.
(The American Farm Bureau Federation (fb.org)
The number of U.S. dairy farms is declining. The COVID-19 pandemic has a hand in the decline of dairy farms throughout the U.S. Before the pandemic, the number of licensed dairy farms declined year after year, with dairy farmers getting out of the business due to reduced prices within the milk industry. The U.S. has just under 32,000 licensed dairy operations.
7. In 2020, the U.S. dairy industry was worth 40.5 billion.
(Statista)
While the COVID-19 pandemic affected the world on many different levels, it impacted the dairy industry, too. While 40.5 billion is substantial, that number is lower than what it could have been. However, when the U.S. dispersed stimulus checks, the dairy industry saw an increase in revenue. The 2021 projected revenue is roughly 722 billion globally.

8. The world consumes 800 million tons of milk each year.
(Our World in Data)
The number of tons of milk consumed globally has doubled over the last 50 years. Even though the number of dairy farms has declined, milk production has increased. This puts a strain on dairy cows; females are overworked and artificially inseminated to produce offspring continually.

Dairy Cow Lifespan and Deaths
9. Over the last decade, the mortality rate of dairy herds ranged from 2% to 15% across the United States.
(Colorado State University)
On-farm dairy cow deaths pose problems, both for the economy and animal welfare. While some farms have a low mortality rate, others suffer significant losses. Cow deaths are complex, with many diagnoses remaining uncertain as to the cause of death.

10. The average natural lifespan of a cow is 15 to 20 years.
(The Humane League.org)
Cows can live long lives under natural conditions, meaning they are not used for milk or beef production. Sadly, once their production drops, they are sent to a slaughterhouse, cutting their life significantly short.
Related: Zebu Cattle
11. The average lifespan for a cow on a dairy farm is 4 to 6 years.
(Compassion in World Farming)

A cow can generate milk for up to 10 months after giving birth. Three months after giving birth, the cow is usually artificially inseminated so she can continue to produce milk. The highest amounts occur during the first three years of the cow’s life. After that point, her milk production begins to drop, and eventually, the cow is slaughtered.
12. Dairy cow slaughters accounted for 9.5% of federally inspected slaughters in 2020.
(USDA)
Livestock Plants that are federally inspected must assure that the plant is in compliance with USDA standards, meaning the cattle is treated humanely and slaughtered humanely.

The Welfare of Dairy Cows
13. The number of cubicles should exceed the number of cows in housing areas by 5%.
(Farm Health Online)
For housing cattle, cubicle space is detrimental to their well-being. Cows need adequate space to lie down and have room, so they don’t soil their bedding. Poor cubicle space leads to udder disease, lameness, and physical damage to the cow. Dairy cows also require access to pasture for grazing.

14. Lameness on U.S. dairy farm cattle ranges from 13% to 55%.
(Science Direct)
Lameness in dairy cattle is an ongoing concern in U.S. dairy farms because this means the cows are in pain. These percentages indicate that approximately 25% to 50% of cows on U.S. dairy farms are in pain, which leads to poor milk production.

Frequently Asked Questions About Dairy Cows
What are dairy cows’ basic needs?
As a rule, there are six basic needs that dairy cattle require.
- Air—Lactating cows’ body temperature rises considerably
- Light—For optimal milk production, cows needs 14 to 16 hours of light per day with at least 6 to 8 hours of darkness
- Space—They need access to food, water, and bedding. Remember that the number of cubicles should exceed the number of cows in housing areas by 5%
- Food—Cows should have access to food 24 hours daily. The feed table should be 4 inches taller than the cows’ feet
- Water—Cows need unlimited access to fresh water daily. Cows need roughly 5 liters in order to eat 1 liter of food per day
- Rest—Concrete floors are harsh on cows. They need soft bedding to lie on. Sand works well and other soft materials
(ABS Global)
Why are cows dehorned?
Cows are dehorned to prevent injury to humans and other cattle. It also allows for a smaller space to house the cow. Dehorning is a painful procedure and has been associated with behavioral and psychological issues in cattle. The cow may have a decline in weight and eating as a result. The methods used for dehorning and disbudding are hot-iron disbudding, chemical disbudding, and amputation dehorning. (FAWEC)
Does Europe have laws that protect the welfare of cows?
Sadly, Europe does not have regulated laws regarding the welfare of cattle. They are only protected under the “General Farm Animals Directive,” meaning farmers should ensure the well-being of the cattle under their care by preventing injury or unnecessary pain and suffering. Since this law is not regulated, enforcing these practices go unfulfilled. (EuroGroup For Animals)
Can you sponsor a dairy cow?
Yes! Through The Cows Foundation, you can sponsor a cow and even pick the one you’d like to help. You have several options on how much financial help you’d like to donate each month, and you’ll receive updates and photos of your cow being cared for in your name. It takes on average $200 a month to properly care for a cow, so any donations are much appreciated. (The Cows Foundation)

Conclusion
Dairy cows play an important role for humans as a food source, but that doesn’t mean they should not be cared for appropriately. This article was meant to bring awareness to the dairy cow’s health and give you resources if you would like to help ensure their health and safety. Not all dairy farms mistreat their cattle, but there is room for improvement, especially in Europe. With the decline in the number of licensed dairy farms, cows are overworked and are under more stress than they should be. If you’d like to help in any way, there are multiple resources that allow you to do so.
Featured Image Credit: Elsemargriet, Pixabay
