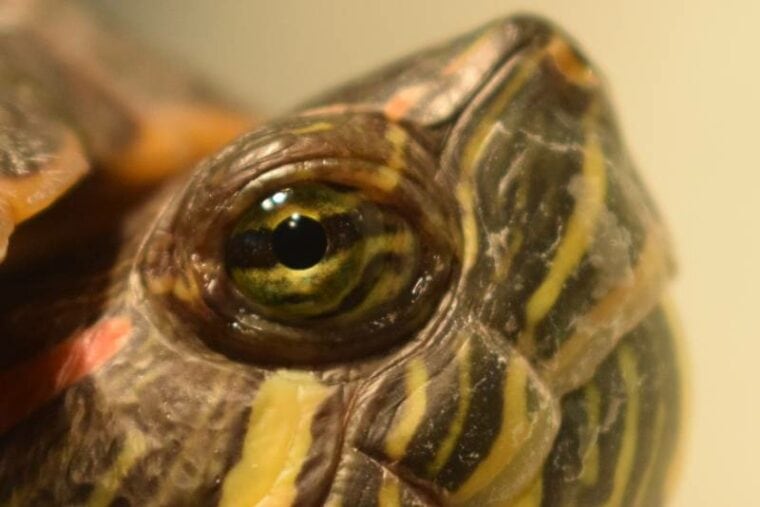

When we think of turtles, we often envision their slow and steady movements, their distinct shells, and their wise, aged appearance. But have you ever wondered about the quality of their eyesight? Do turtles have good eyesight? Turtles have a great sense of vision that perfectly suits their needs! While their eyesight may not be as sharp, turtles use their vision to navigate and sense movements in their surroundings instead of fine details.
Still curious about turtles’ eyesight? Read on as we uncover turtles’ visual capabilities, comparing them to other creatures, and delving into their unique characteristics!
Turtle Eyes Explained
Like most animals including humans, turtles possess a pair of eyes, each located on the sides of their head, which gives them a panoramic view. Their eyes are protected by a transparent covering called the cornea, which acts as the outermost layer. Beneath the cornea lies the iris, the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye through the pupil, the hole in the middle. Turtles also have a lens that focuses incoming light onto the retina, a layer of specialized cells at the back of the eye responsible for converting light into electrical signals.
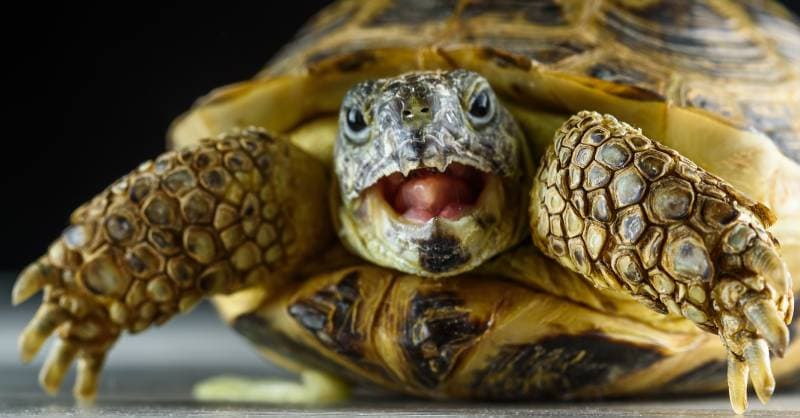

How Do Turtles See?
Turtles predominantly rely on their vision to navigate their surroundings. They have a relatively wide field of vision, which allows them to see objects and movements occurring both in front of them and on the periphery, making it easier for them to spot potential predators or prey.
How Good Is Turtle Eyesight?
While turtles have a wide field of vision, their visual acuity is thought to be not as sharp as that of humans. They have the ability to see over and below the water’s surface. Turtles are capable of distinguishing between objects and differentiating between various light levels.
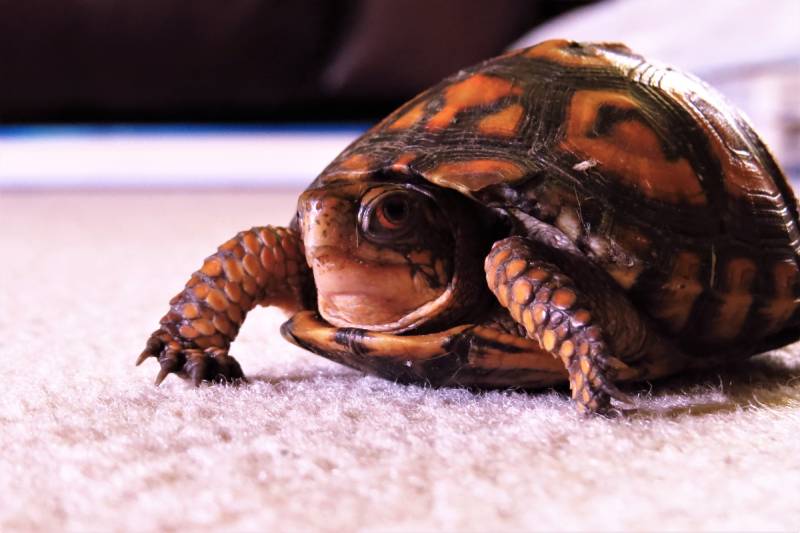

Turtle Eyesight vs. Humans
Compared to humans, turtles have a different visual experience. Humans possess a higher visual acuity, enabling us to perceive intricate details and possibly enjoy a more vibrant and colorful world. Turtles, on the other hand, have panoramic vision and the ability to see the glow of their bioluminescent prey.
However, it’s important to note that while turtles’ eyesight may not be as sharp as ours, it perfectly suits their needs and allows them to survive in their natural habitats.
Turtle Eyesight vs. Other Reptiles
Among reptiles, turtles’ eyesight falls somewhere in the middle. Some reptiles, such as snakes, possess limited visual capabilities, relying heavily on other senses such as heat detection or vibrations. Conversely, certain lizards, like chameleons, have incredibly sharp eyesight and can see a wide spectrum of colors. Turtles, with their moderate visual abilities, strike a balance between these two extremes.

Turtle Eyesight vs. Cats and Dogs
When comparing turtle eyesight to that of cats and dogs, there are notable differences in their visual capabilities. Cats and dogs have evolved to possess superior eyesight compared to turtles. Both cats and dogs have predatory ancestry with a keen sense of depth perception thanks to their front-located eyes and the ability to see fine details. They also have great night vision, allowing them to navigate in very low-light conditions.
It’s important to remember that each species has unique adaptations that suit their specific needs and habitats, and turtles’ eyesight is well-suited for their particular lifestyles.
Turtle Eyesight vs. Tortoise Eyesight
Turtles and tortoises belong to the same family, but they have some key differences in their eyesight. While both have similar visual acuity, tortoises generally have a more limited field of vision compared to turtles. This difference is due to the variation in their habitats and lifestyles.
Turtles, often found near bodies of water, require a broader field of vision to monitor potential threats and prey. In contrast, tortoises, who primarily inhabit land, have a narrower field of vision but are more adept at recognizing objects directly in front of them.


Do Turtles Have Night Vision?
Turtles do not have night vision like cats or other animals that hunt at night, but they can perceive their surroundings even in low-light conditions.
Their eyes contain specialized cells called rods, which are highly sensitive to dim light. This adaptation allows them to perceive objects in the dark, although their vision may be less precise compared to daylight conditions. It’s worth mentioning that some turtle species, such as the marine leatherback turtle, have even better night vision due to their deep-sea foraging habits.
Do Turtles See Colors?
While turtles don’t see colors in the same way as humans, they do have some color vision. Turtles were once thought to have limited color vision, but recent research has shown that they have tetrachromatic color vision, which means they can see within the ultraviolet visual range. They can distinguish between certain colors, and some have a preference for blue in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. Experiments have proved that they can distinguish between blue, green, yellow, and red. However, it is unclear how vibrant these colors may appear to them.

How About Their Eyesight Underwater?
Turtles’ eyesight underwater is surprisingly well-adapted to their aquatic lifestyle. Their eyes have special features that enable them to see clearly in water. The refractive index of their cornea and lens matches that of water, reducing distortions and allowing for better focus.
Their eyes also have a protective membrane called the nictitating membrane, which acts as a built-in pair of goggles, shielding their eyes from debris and providing clear vision. With these adaptations, turtles can navigate underwater environments with relative ease, relying on their visual acuity to locate prey, avoid predators, and explore their watery world.
Common Eye Problems for Turtles
Like any living creature, turtles can also experience eye problems. Common issues include eye infections, injuries, and corneal ulcers. If you notice any changes in your pet turtle’s eyes, such as cloudiness, discharge, or puffiness. Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent further complications and ensure the well-being of your turtle.

Final Thoughts
In conclusion, turtles have a unique visual perception that suits their evolutionary needs. While their eyesight may not rival that of humans or some other animals, they have adapted to their surroundings remarkably well. With their broad field of vision, the ability to detect movement, and some degree of night vision, turtles excel in their natural habitats. So, the next time you encounter a turtle, appreciate the world they perceive through their eyes—a world that may be less vibrant but holds its own charm and purpose.
Featured Image Credit: decography, Shutterstock








