Click to Skip Ahead
When you’re looking to give a little bunny a forever home, it helps to know the differences between females and males. If you find out the sex of the rabbit you keep as a pet, you’ll be able to weigh the advantages and disadvantages, and it’ll even make it easier to care for them and deal with any health issues that might crop up.
While male and female rabbits are pretty similar, a few differences will help you determine which gender is right for you. Below, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about male and female rabbits.
Visual Differences

At a Glance
Rabbits 101
Rabbits are fluffy, adorable creatures that hop along the bunny trail at Easter and have worked their way into many books, movies, and TV shows. In fact, in Southeastern Native American Folklore, rabbits are known for being quite the tricksters.
Rabbits come in many shapes and sizes, but all have a distinct personality that is uniquely their own. There are nearly 50 breeds of domestic rabbits to choose from when searching for a pet.
However, male and female rabbits don’t look all that different regarding appearance, so it can be hard to tell which is the male and which is the female. You’ll need to examine your rabbit’s genitals to determine which gender your furry friend is. If your rabbit does not tolerate handling and you can’t determine its sex, you can make an appointment with your vet to find out.
You need to determine the sex of your rabbit so that you can take care of it properly. We’ll give you an overview of the personality, training needs, health issues, and pros and cons of the male and female rabbits in our next sections.
Male Rabbit Overview
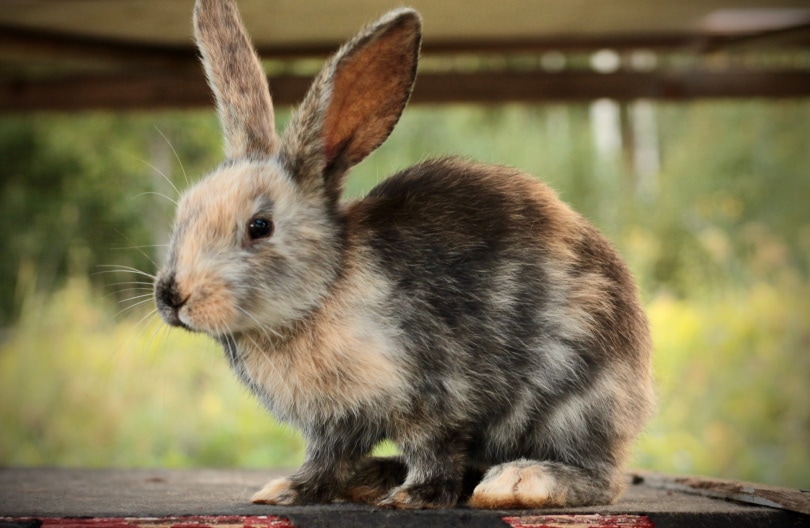

A male rabbit is called a buck and, believe it or not, is more laidback and gentler than its female counterpart will ever be.
Personality / Character
Male rabbits are considered more laidback and gentler than female rabbits. They make good pets and don’t mind being held. However, every rabbit has a distinct personality, and some breeds take longer to warm up to their owners than others.
Training
Male rabbits are considered to be easier to train than female rabbits. They are the best choice for beginning rabbit keepers and can be taught to use a litter box and respond to their names. They get into less trouble and tend to be less destructive than their female counterparts. This is especially true for male rabbits who have been neutered, and it’s also cheaper to have males fixed than females.
Health & Care
While male and female rabbits are susceptible to the same health issues, including gut stasis, respiratory issues, and fly strike, males are more likely to suffer from these conditions:

Breeding
You should have your male rabbit neutered unless you plan on breeding rabbits. It’s healthier for the rabbit and may prevent aggressive tendencies. Also, a rabbit that has not been neutered will spray, can be protective of female rabbits, and will mount every object it can find, including females.
Female Rabbit Overview

The female rabbit is called a doe and is not quite as sweet as her male counterpart. Although they’re similar in many ways, we’ll discuss a few of the differences below.
Personality / Character
A female rabbit is more territorial than a male and may actually lunge at you when you try to touch her. However, that is usually only when the female thinks you are invading her space, and they rarely bite. Some females will try to exert dominance over the males, and although they’re not as gentle, female rabbits make excellent pets. They take longer to get comfortable in a new environment, but eventually, a female will settle down and grow more confident around her owners.
Training
Training a female rabbit isn’t as easy as training a male rabbit is. Since the rabbit is territorial and likes to be dominant, she also likes to be in control and will overtake your home if you let her. You can train a female, but it’s best if they are raised with an experienced rabbit keeper instead of a beginner.
Health & Care
Although females are more vulnerable to some health issues, getting them spayed can reduce the likelihood they’ll contract them.

Breeding
Breeding a female rabbit is pretty easy since rabbits are prolific breeders. If you don’t have your female spayed, she could have false pregnancies and run a greater risk of developing uterine cancer. If you see your rabbit mounting the male in your hutch, it is because she’s trying to exert dominance.
Conclusion
When choosing which rabbit is right for you, it’s best to research several breeds. If you’re an expert rabbit keeper, the female might work well for you, especially if you’re looking to breed. However, the male is best for a beginning rabbit owner since they are more laid back and gentler. Whichever rabbit you choose, make sure that you get them spayed or neutered unless you’re going to breed them. Regardless of their sex, rabbits make excellent pets as long as you treat them well.
- You Might Also Be Interested In: Wild vs. Domestic Rabbits
Featured Image Credit: (L) erica joy manliquez, Shutterstock | (R) Macy Cowan, Shutterstock










